Difference between revisions of "Custom Personality Tutorial"
(→Nesting String) |
|||
| Line 76: | Line 76: | ||
views = tutorialView | views = tutorialView | ||
| − | |||
nesting = document/text.story | nesting = document/text.story | ||
[main:tutorialView] | [main:tutorialView] | ||
| − | |||
xmlEncode = 0 | xmlEncode = 0 | ||
| − | accepted = | + | accepted = text.story |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| Line 106: | Line 101: | ||
We'll be processing InDesign documents, which have a 'natural' hierarchy: documents contain stories, stories contain paragraphs, paragraphs contain text runs, text runs contain words. | We'll be processing InDesign documents, which have a 'natural' hierarchy: documents contain stories, stories contain paragraphs, paragraphs contain text runs, text runs contain words. | ||
| − | + | This is not the only hierarchy we could use in InDesign documents. An alternate hierarchy would be documents contain spreads, spreads contain text frames, text frames contain text runs, text runs contain words. | |
| + | |||
| + | This alternate hierarchy does not 'map' onto the first hierarchy: text frames do not map cleanly onto paragraph boundaries or vice versa. | ||
In this case, we're initially interested in getting the text, and we don't care too much about the lower level granules, so all we tell the [[Disassembler|''disassembler'']] is: | In this case, we're initially interested in getting the text, and we don't care too much about the lower level granules, so all we tell the [[Disassembler|''disassembler'']] is: | ||
| Line 114: | Line 111: | ||
This tells the [[Disassembler|''disassembler'']]: if you see a <code>document</code> granule, please disassemble it into <code>text.story</code> granules. | This tells the [[Disassembler|''disassembler'']]: if you see a <code>document</code> granule, please disassemble it into <code>text.story</code> granules. | ||
| − | When presented with a document granule, the [[Disassembler|''disassembler'']] will spit out a few story granules, followed by the original document granule. | + | When presented with a document granule, the [[Disassembler|''disassembler'']] will spit out a few story granules, followed by the original document granule. [[Disassembler|''disassembler'']] never take granules away: they only add to the input stream so the original document granule will still be output, but it will be preceded by the text.story granules from the document. |
Later on, we'll tell the disassembler to dig deeper than that. | Later on, we'll tell the disassembler to dig deeper than that. | ||
| − | == Class Identifier Shorthand == | + | == Granule Class Identifier Shorthand == |
| − | The <code>nesting</code> entry is a slash-separated list of [[Class identifier|''class identifiers'']]. The expression | + | The <code>nesting</code> entry is a slash-separated list of [[Class identifier|''class identifiers'']], which represent some granule classes. The expression |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| Line 139: | Line 136: | ||
because Crawler allows granule class identifiers to be shortened by dropping the <code>com.rorohiko.granule.</code> prefix. | because Crawler allows granule class identifiers to be shortened by dropping the <code>com.rorohiko.granule.</code> prefix. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Log Output == | == Log Output == | ||
| Line 177: | Line 160: | ||
We can see the [[OutputTextFile|''OutputTextFile'']] adapter is unhappy (<code>Error: OutputTextFile.prototype.dumpData_protected_: needs file</code>) because it does not know where it needs to send its output. We'll fix that soon. | We can see the [[OutputTextFile|''OutputTextFile'']] adapter is unhappy (<code>Error: OutputTextFile.prototype.dumpData_protected_: needs file</code>) because it does not know where it needs to send its output. We'll fix that soon. | ||
| − | The area of interest are the granules that | + | The area of interest are the granules that trickled through the adapter network: we can see we had two story granules, followed by a document granule. |
| − | == Getting | + | == Getting The Text Into a File == |
We'll now modify the personality-level config.ini a little bit so the text gets dumped into a file. | We'll now modify the personality-level config.ini a little bit so the text gets dumped into a file. | ||
| − | The sub-adapters used in the [[ViewExporter|''ViewExporter'']] in Crawler look at a number of predefined [[Context Variable|''context variables'']] to determine what to do | + | The sub-adapters used in the [[ViewExporter|''ViewExporter'']] in Crawler look at a number of predefined [[Context Variable|''context variables'']] to determine what to do. |
| − | The [[OutputTextFile|''OutputTextFile'']] adapter will query the context for a [[Context Variable|''variable'']] called <code>FILEPATH</code>. If this [[Context Variable|''variable'']] is defined and contains a path to a file, then it the [[OutputTextFile|''OutputTextFile'']] adapter will dump its output into that file. | + | One of these many predefined variables is called <code>FILEPATH</code>. |
| + | |||
| + | The [[OutputTextFile|''OutputTextFile'']] adapter will query the context for a [[Context Variable|''variable'']] called <code>FILEPATH</code>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | If this [[Context Variable|''variable'']] is defined and contains a path to a file, then it the [[OutputTextFile|''OutputTextFile'']] adapter will dump its output into that file. | ||
We can set the <code>FILEPATH</code> variable in the 'global' app context for the application by means of the personality-level [[INI file|''config.ini'']] file. | We can set the <code>FILEPATH</code> variable in the 'global' app context for the application by means of the personality-level [[INI file|''config.ini'']] file. | ||
| Line 206: | Line 193: | ||
[main:tutorialView] | [main:tutorialView] | ||
| − | |||
xmlEncode = 0 | xmlEncode = 0 | ||
| + | |||
accepted = document, text.story | accepted = document, text.story | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
The added entry ''FILEPATH = ...'' in the [appContextData] section defines a context variable <code>FILEPATH</code>. | The added entry ''FILEPATH = ...'' in the [appContextData] section defines a context variable <code>FILEPATH</code>. | ||
| − | This value is picked up by the [[OutputTextFile|''OutputTextFile'']] adapter inside the [[ViewExporter|''ViewExporter'']]. | + | This value is picked up by the [[OutputTextFile|''OutputTextFile'']] adapter embedded inside the [[ViewExporter|''ViewExporter'']]. |
Run the <code>Export.jsxbin</code> again. | Run the <code>Export.jsxbin</code> again. | ||
| Line 225: | Line 208: | ||
== Book Files == | == Book Files == | ||
| − | Now close all documents, and open just an InDesign book file. | + | Now close all documents, and open or create just an InDesign book file that references a few InDesign files. |
| − | + | Keep all documents closed; only the book file should be open. | |
| − | You might | + | Run the <code>Export.jsxbin</code> again. |
| + | |||
| + | This time, you should end up with the collated text from all the book's documents concatenated together. | ||
| + | |||
| + | You might wonder how this could possibly work, given that the nesting in the config file does not mention book granules. You might expect that you would have needed to change the config.ini to read: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| Line 236: | Line 223: | ||
nesting = book/document/text.story | nesting = book/document/text.story | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | meaning: | ||
* start from a book | * start from a book | ||
| Line 241: | Line 230: | ||
* descend into the text stories in each document | * descend into the text stories in each document | ||
| − | + | This longer nesting string <code>book/document/text.story</code> would also work for processing books, but it would not work for single documents. | |
| − | The nesting string <code>document/text.story</code> | + | When processing a single document, the initial granule that starts the process is a document, not a book. The nesting string <code>book/document/text.story</code> wants to see a book granule before it starts 'digging in'. |
| − | The | + | The shorter nesting string <code>document/text.story</code> is better, because it works for both books and documents. |
| − | + | The underlying mechanism works as follows: when we run ''Export.jsxbin'', a granule comes down the line to be processed. It will be either a book granule or a document granule. | |
| − | + | When it is a document granule, we get a match with the top-level nesting element, and the disassembly process can properly start. | |
| − | + | If it is a book granule, there is no matching granule class at the start of the nesting string <code>document/text.story</code>. | |
| − | Each of these | + | When that happens, the ''ViewExporter'' will try to automatically pick a default approach to disassemble. We're not telling it what it should do with book granules, so it 'makes something up'. |
| + | |||
| + | For books, it will disassemble the book into its component document granules, and then process these document granules one by one. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Each of these document granules will then also be presented to the ViewExporter. | ||
| + | |||
| + | These granules do match the starting entry of the nesting string <code>document/text.story</code> and the 'normal' document disassembly will take its course from there on. | ||
== Nesting String == | == Nesting String == | ||
| Line 272: | Line 267: | ||
[main:tutorialView] | [main:tutorialView] | ||
| − | |||
xmlEncode = 0 | xmlEncode = 0 | ||
| − | accepted | + | accepted = text.word |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | There are | + | There are two changes: the ''nesting'' string now mentions ''text.word'' instead of ''text.story'' and the ''accepted'' entry now lists ''text.word'' instead of ''text.story'. |
| − | This setup will grab an incoming input granule (either a document or a book granule), and peel it apart, layer by layer, until it reaches the individual words. | + | This setup will grab an incoming input granule (either a document or a book granule), and then gradually peel it apart, layer by layer, until it reaches the individual words hidden inside. |
| − | The 'defaulting' mechanism mentioned in the previous section also occurs each time we have unmatched elements in the nesting string. | + | The 'defaulting' mechanism mentioned in the previous section also occurs each time we have unmatched elements in the middle of the nesting string. |
| − | Essentially, the ''ViewExporter'' will 'dig deeper' into the data, disassembling level by level, until it 'hits' the desired granule | + | Essentially, without instructions from the ''nesting'' string, ''ViewExporter'' will try to 'dig deeper' into the data, disassembling level by level, until it either 'hits' the desired granule class, or comes up empty. |
| − | When a ''document'' is disassembled, the ViewExporter will try to match the next required granule | + | When a ''document'' is disassembled, the ViewExporter will try to match the next required granule class shown in the ''nesting'' string. In this example that granule class is ''text.word''. |
| − | Documents don't disassemble readily into words. | + | Documents don't disassemble readily into words. So, the defaulting mechanism kicks in, and the document is disassembled into some smaller granules. The default ViewExporter behavior is to disassemble a document into ''spread'' granules. |
| − | ViewExporter will now try to try to disassemble these ''spread'' granules to the desired ''text.word'' granule | + | ViewExporter will now try to try to disassemble these ''spread'' granules to the desired ''text.word'' granule class. |
| − | Just | + | Just as with ''document'' granules, ''spread'' granules don't split up into words, so it will again have to call on some default behavior. |
| − | + | The default is to disassemble a ''spread'' granule into frame granules. Some, but not necessarily all, of these frames will be text frames. | |
| − | + | ViewExporter will now try to try to disassemble these ''frame'' granules to the desired ''text.word'' granule class. | |
| − | For text frames, it will finally work: ''ViewExporter'' | + | For image frames, that won't work. It will try digging a bit deeper using the same defaulting mechanism at each 'level', but eventually it'll come up empty: there are no word granules to be found in an image frame. |
| + | |||
| + | For text frames, it will finally work: ''ViewExporter'' does know how to grab the contents of a text frame and disassemble it into words. | ||
This finally satisfies the nesting string which was calling for ''text.word'' granules. | This finally satisfies the nesting string which was calling for ''text.word'' granules. | ||
| − | As the | + | As the complete nesting string has now been matched, no further disassembly takes place. It will not try to disassemble the ''text.word'' granules any further. |
| + | |||
| + | For an InDesign document the nesting string <code>document/text.word</code> is more or less equivalent to a nesting string <code>document/spread/text.frame/text.word</code>. | ||
| − | + | The main difference is that we leave it up to the ''ViewExporter'' to figure out how it will get from ''document'' granules down to ''text.word'' granules. | |
| − | + | In the log file you'll see something like: | |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
************************** | ************************** | ||
Revision as of 01:57, 16 January 2014
First, we'll build a very simple personality, and we'll gradually extend it to better demonstrate how Crawler works.
The basis of nearly all document conversion personalities is the ViewExporter adapter.
The ViewExporter is a complex adapter. Basically, it connects two 'main' sub-adapters: a disassembler (which breaks a document granule into smaller granules) and an assembler (which takes the granules coming out of the disassembler, and builds the desired end-result).
The disassembler is part of the default Crawler setup. When running Crawler, the ViewExporter will ask the currently active application to provide it with an appropriate disassembler, and it will then use that disassembler in the ViewExporter.
The disassembler gets further configuration through the configuration files.
Contents
Adjusting The Top-Level config.ini
First, we'll enhance the top-level configuration file so it knows about the new personality we're going to build.
Let's call the personality 'tutorial'.
Change the top-level config.ini (i.e. the config.ini which resides next to Export.jsxbin). Initially it it looks similar to this (I've omitted most comments for brevity).
[conditionals] selectors = text [main] personalityConfig?text = "./Personalities/Text/config.ini" # ******************************************************************************** [debug] debugMonitoring = false logLevel = 0
Change it so it becomes like this:
[conditionals] selectors = tutorial [main] personalityConfig?tutorial = "./Personalities/Tutorial/config.ini" personalityConfig?text = "./Personalities/Text/config.ini" # ******************************************************************************** [debug] debugMonitoring = true monitorAdapters = inputSplitter logLevel = 5 logFileName = Crawler.log
This tells Crawler that we want to select 'tutorial', and it also says that the personalityConfig entry needs to be the lower-level config.ini inside the Tutorial folder inside the Personalities folder.
We also switch on debug monitoring, and hook a Debug Monitor into the inputSplitter adapter inside the ViewExporter.
Creating A Tutorial Personality
Now that Crawler 'knows' about the new personality, the next step is to make a start building it.
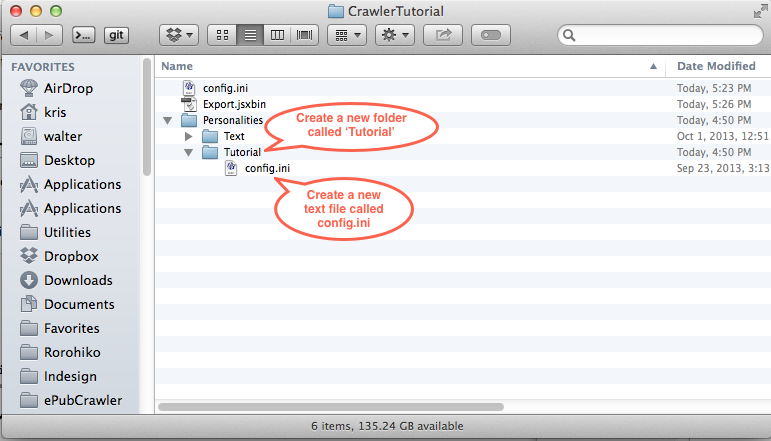
Open the Personalities folder, and create a new subfolder called Tutorial. Inside that subfolder, create a text file called config.ini.
Put the following text in this personality-level config.ini file:
[main] views = tutorialView nesting = document/text.story [main:tutorialView] xmlEncode = 0 accepted = text.story
View
With this config file, we tell the ViewExporter that we only need a single view, named tutorialView.
Later on, we'll build personalities with multiple views. Views are a way to concurrently build separate, but related files.
For example, when converting to XHTML, we need to build a CSS structure as well as an XHTML structure, and keep track of how they relate to one another.
This kind of 'interrelated' file building is handled through views in Crawler.
For this first tutorial, we don't have a need to build multiple views concurrently, so we can make so with just the single tutorialView.
Disassembly Hierarchy
We'll be processing InDesign documents, which have a 'natural' hierarchy: documents contain stories, stories contain paragraphs, paragraphs contain text runs, text runs contain words.
This is not the only hierarchy we could use in InDesign documents. An alternate hierarchy would be documents contain spreads, spreads contain text frames, text frames contain text runs, text runs contain words.
This alternate hierarchy does not 'map' onto the first hierarchy: text frames do not map cleanly onto paragraph boundaries or vice versa.
In this case, we're initially interested in getting the text, and we don't care too much about the lower level granules, so all we tell the disassembler is:
nesting = document/text.story.
This tells the disassembler: if you see a document granule, please disassemble it into text.story granules.
When presented with a document granule, the disassembler will spit out a few story granules, followed by the original document granule. disassembler never take granules away: they only add to the input stream so the original document granule will still be output, but it will be preceded by the text.story granules from the document.
Later on, we'll tell the disassembler to dig deeper than that.
Granule Class Identifier Shorthand
The nesting entry is a slash-separated list of class identifiers, which represent some granule classes. The expression
[main] ... nesting = document/text.story ...
is actually shorthand for:
[main] ... nesting = com.rorohiko.granule.document/com.rorohiko.granule.text.story ...
because Crawler allows granule class identifiers to be shortened by dropping the com.rorohiko.granule. prefix.
Log Output
Our rudimentary personality is not complete yet, but we can already try to run it. We won't get any meaningful output just yet, but we've configured a debug monitor, and a log file, so we'll see some useful information there.
If you run the Export.jsxbin script on an InDesign document, you'll get something like this in the Crawler.log file that should appear next to the Export.jsxbin file:
Mon Dec 30 2013 18:02:18 GMT+1300: Error: OutputTextFile.prototype.dumpData_protected_: needs file Mon Dec 30 2013 18:02:18 GMT+1300: Note : ViewSplitter 'inputSplitter' input log: ************************** InDesignStoryGranule [Facesti quo tet, offictation reculpa ritiand icatum doles maios re ...] InDesignStoryGranule [Pudipsunt alitionet que labo. Liquo cor rerundelento eos et apiet ...] InDesignDocumentGranule [TutorialTest.indd] ************************** Mon Dec 30 2013 18:02:18 GMT+1300: Error: OutputTextFile.prototype.dumpData_protected_: needs file
We can see the OutputTextFile adapter is unhappy (Error: OutputTextFile.prototype.dumpData_protected_: needs file) because it does not know where it needs to send its output. We'll fix that soon.
The area of interest are the granules that trickled through the adapter network: we can see we had two story granules, followed by a document granule.
Getting The Text Into a File
We'll now modify the personality-level config.ini a little bit so the text gets dumped into a file.
The sub-adapters used in the ViewExporter in Crawler look at a number of predefined context variables to determine what to do.
One of these many predefined variables is called FILEPATH.
The OutputTextFile adapter will query the context for a variable called FILEPATH.
If this variable is defined and contains a path to a file, then it the OutputTextFile adapter will dump its output into that file.
We can set the FILEPATH variable in the 'global' app context for the application by means of the personality-level config.ini file.
Contexts are arranged in a hierarchy; the 'topmost' context is the app context which we can influence from the config.ini file.
Change the config.ini in the Tutorial directory so it becomes:
[main] views = tutorialView nesting = document/text.story [appContextData] FILEPATH = ~/Desktop/output.txt [main:tutorialView] xmlEncode = 0 accepted = document, text.story
The added entry FILEPATH = ... in the [appContextData] section defines a context variable FILEPATH.
This value is picked up by the OutputTextFile adapter embedded inside the ViewExporter.
Run the Export.jsxbin again.
You should now end up with a file called output.txt on the desktop. This file will contain all the text extracted from the InDesign document.
Book Files
Now close all documents, and open or create just an InDesign book file that references a few InDesign files.
Keep all documents closed; only the book file should be open.
Run the Export.jsxbin again.
This time, you should end up with the collated text from all the book's documents concatenated together.
You might wonder how this could possibly work, given that the nesting in the config file does not mention book granules. You might expect that you would have needed to change the config.ini to read:
[main] ... nesting = book/document/text.story
meaning:
- start from a book
- descend into the documents
- descend into the text stories in each document
This longer nesting string book/document/text.story would also work for processing books, but it would not work for single documents.
When processing a single document, the initial granule that starts the process is a document, not a book. The nesting string book/document/text.story wants to see a book granule before it starts 'digging in'.
The shorter nesting string document/text.story is better, because it works for both books and documents.
The underlying mechanism works as follows: when we run Export.jsxbin, a granule comes down the line to be processed. It will be either a book granule or a document granule.
When it is a document granule, we get a match with the top-level nesting element, and the disassembly process can properly start.
If it is a book granule, there is no matching granule class at the start of the nesting string document/text.story.
When that happens, the ViewExporter will try to automatically pick a default approach to disassemble. We're not telling it what it should do with book granules, so it 'makes something up'.
For books, it will disassemble the book into its component document granules, and then process these document granules one by one.
Each of these document granules will then also be presented to the ViewExporter.
These granules do match the starting entry of the nesting string document/text.story and the 'normal' document disassembly will take its course from there on.
Nesting String
Change the config.ini to look as follows:
[main] views = tutorialView nesting = document/text.word [appContextData] FILEPATH = ~/Desktop/output.txt [main:tutorialView] xmlEncode = 0 accepted = text.word
There are two changes: the nesting string now mentions text.word instead of text.story and the accepted entry now lists text.word instead of text.story'.
This setup will grab an incoming input granule (either a document or a book granule), and then gradually peel it apart, layer by layer, until it reaches the individual words hidden inside.
The 'defaulting' mechanism mentioned in the previous section also occurs each time we have unmatched elements in the middle of the nesting string.
Essentially, without instructions from the nesting string, ViewExporter will try to 'dig deeper' into the data, disassembling level by level, until it either 'hits' the desired granule class, or comes up empty.
When a document is disassembled, the ViewExporter will try to match the next required granule class shown in the nesting string. In this example that granule class is text.word.
Documents don't disassemble readily into words. So, the defaulting mechanism kicks in, and the document is disassembled into some smaller granules. The default ViewExporter behavior is to disassemble a document into spread granules.
ViewExporter will now try to try to disassemble these spread granules to the desired text.word granule class.
Just as with document granules, spread granules don't split up into words, so it will again have to call on some default behavior.
The default is to disassemble a spread granule into frame granules. Some, but not necessarily all, of these frames will be text frames.
ViewExporter will now try to try to disassemble these frame granules to the desired text.word granule class.
For image frames, that won't work. It will try digging a bit deeper using the same defaulting mechanism at each 'level', but eventually it'll come up empty: there are no word granules to be found in an image frame.
For text frames, it will finally work: ViewExporter does know how to grab the contents of a text frame and disassemble it into words.
This finally satisfies the nesting string which was calling for text.word granules.
As the complete nesting string has now been matched, no further disassembly takes place. It will not try to disassemble the text.word granules any further.
For an InDesign document the nesting string document/text.word is more or less equivalent to a nesting string document/spread/text.frame/text.word.
The main difference is that we leave it up to the ViewExporter to figure out how it will get from document granules down to text.word granules.
In the log file you'll see something like:
************************** Thu Jan 16 2014 14:07:30 GMT+1300: Note : ViewSplitter 'inputSplitter' input log: ************************** InDesignWordGranule [Pudipsunt] InDesignWordGranule [alitionet] InDesignWordGranule [que] InDesignWordGranule [labo.] ... InDesignWordGranule [que] InDesignWordGranule [vel] InDesignWordGranule [molest] InDesignTextFrameGranule [Pudipsunt alitionet que labo. Liquo cor rerundelento eos et apiet dende arum aliquos ipit qui ditiusa eriam, cupti antiis vendignis et derferum et offictiatem quatus everspis et aut aut erferfe rspelig eniscipit aut eiciassi tet ute peror aut etur ratur ratenist quatium aut odignamet est, sequiatures eos moloren dantin re occaescium none cupiet aut officie nihita plabori temporem ipsanduntur? Ihilignam, consequis assitiis pore, nonsendus expla niscitia consequiam est, comnia simos nus, sunt doloria cumque peruptatet inverunt. Faceati officabo. Loreper iorrum esti venisciis magnam renihit volor molland elenem aris non comnimin re porrora dolectas endic tem enihitio et lit modis acerite pore consernatem. Ga. Soluptatur accus quia volut quat preperi dolorro bla quaspe nectet que none nos ipidempor aliquiam vellore nusdame ndunt, iurest, te moleste mpore, niminctem asita non perovidel ipit alibusd andeni ommoluptibus quat ese nisquos quo enda num qui odicimpores alibus, illenda quiam fuga. Et velibus exera sum ate sedisitatias earciassunt vid excea quaepudit, comnia aliquas perchit ectest, cullaborum et quidelendia aut volorru ntiunto ipid quod ut alibusae sim quat ex exerest adi idis dolorib eruptati denis que vel molest] InDesignWordGranule [Facesti] ... InDesignTextFrameGranule [Facesti quo tet, offictation reculpa ritiand icatum doles maios re sime niet ma consequae pelignimus doluptia planihi ctorae pro in perum ius est vel int. Inulpa si tem sundaec tinctur secuptaecea pelitat iorest, accum iducient, utes aut mos modis ad que pernamus aut mo optae voloreptate pe pellaut que volo eaqui omnis eaque quatur aut mo to quaectur, conet aspel evelest am que nem essum aliquidiam enis invelestio to testi quae nonsect ibusda nonecus estis solorernam et quiscim agnimi, in pro is volor sit exces eum qui nobitet ut re volupti orporeris alibus aut aut laut entum et qui aditaturem volorer ibusam quatem rehent excessi blaute dolorepro bero omniend igentis quianienis expliqu idellabo. Ume quatecta doluptat eum autentotae solut dolupta spidus non nullupt aquamusa qui dionsequiae. Et hil ipsapist quo totata volorei cture, sed molore evellig nimilis prae secus molorum anda sediti accus preperi aspero volor aut rendion por minimus reperum reces eat es nim nulparunt, cum rem rero consequiaspe voloriate post, sumenimagnis rerupti doloreperiat listo comnim quiatur, que re pratur? Quiae nimus aute nobitassimi, quundellori core, cones nos ad et et velent accabo. Et lit volute eum lique nihicim poressiti adite velitat la voloribus, sumet ipsum faccabo. Ut ut officium diaeria ne aut vellupiti] InDesignSpreadGranule [Spread #1] InDesignDocumentGranule [TutorialTest2.indd] **************************
Reading back to front, you can see that a document is broken up into spreads, spreads are broken up into frames, and the text frames are broken up into words.
Assembling
As these granules come 'down the pipe' we need to re-assemble them again into some kind of output.
That's where the accepted comes in: the tutorialView accepts text.word granules. In other words: of all the granules we see in the log file, only the text.word granules are 'let through' into the view.
The output file will not look as good as before: all words will be running together without intervening spaces.
Changing the source disassembly
Currently, the source document is disassembled in story order: the disassembler goes into the document, then enumerates all the stories:
[main] ... nesting = document/text.story